- +61 7 3374 2877
- Email Us
This article defines Flicker and its associated measurement indices, describing how Flicker is generated and mitigated. Causes and mitigation of Flicker produced by wind turbines are also briefly explored.
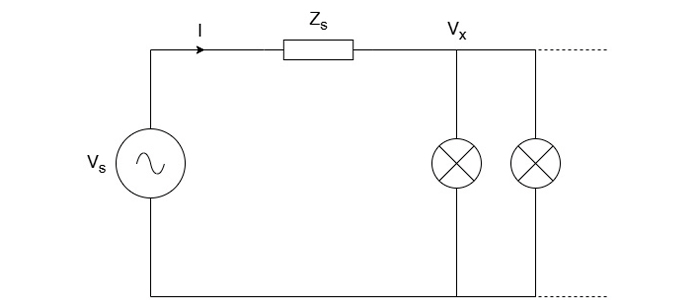
Consider the circuit in Figure 1 consisting of a voltage source Vs with an associated system impedance Zs that is connected to a load consisting of a network of incandescent lights.
The voltage across the light network Vx is given by equation 1.
Vx = Vs – Zs I … (1)
A changing load current ∆I yields a change in voltage ∆Vx across the load which is proportional to the system impedance Zs given in equation 2. A fluctuating voltage across the light network will result in fluctuations in light intensity.
∆Vx = – Zs ∆I … (2)
Flicker describes the perceivable fluctuation of light intensity to the human eye. Its presence can lead to irritability, fatigue, migraines, loss of concentration and in some cases trigger epileptic fits in vulnerable people [2].
Causes of flicker are generally any large-draw varying loads such as electric arc furnaces, induction motors with high inrush currents, wind turbines and ovens etc.
Flicker Indices
Figure 2 illustrates the level of perception of light flicker from a 60W incandescent bulb. The sensitivity is a function of the frequency of the voltage fluctuations and is also dependant on the voltage level of the lighting. The acceptable regions are below the curves.
It is based on studies which measured when the majority of participants were irritated by fluctuations in the light intensity of a 230V/120V, 60W incandescent light (as was commonly used in Europe at the time [3]).
Two severity indices are utilised (IEC 61000-4-15 [1]):
Short term flicker Pst: Quantifies flicker severity over 10 minutes and is useful for assessing disturbances caused by individual sources with short duty-cycles [1]. Normalised to 1.0, a Pst value of 1.0 corresponds to flicker severity that irritates 50% of the population [2].
Long term flicker Plt: Quantifies flicker severity over 2 hours. It is useful for assessing flicker severity from equipment with long and variable duty cycles (e.g. arc furnaces) [1]. It is recommended the value be less than 0.65 [4] or 0.8 [5] in low voltage systems.
